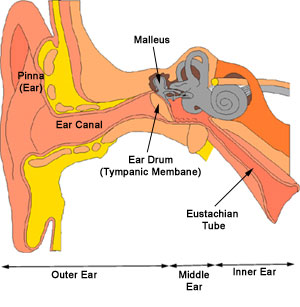
Otitis externa (swimmers ear)
Otitis externa is a common condition affecting people of all ages in which there
is infection or inflammation of the external ear and/or the ear canal. There
are a number of possible causes:
- it may be part of a more general skin problem, such as eczema or psoriasis;
- bacterial or fungal infection;
- prolonged exposure to water;
- trauma from scratching or foreign objects in the ear;
- swimming in polluted water;
- attempting to clean the ear canal with cotton swabs or small objects,
can irritate the skin. Remember the lining of the canal of the ear is lined
with
special
cells that migrate to the outside, moving the wax out. You donít need
to remove the wax with cotton buds, you are more likely to push the wax onto
the ear drum
- hair spray, hair dyes, shampoos, and other chemicals may irritate the
skin of the ear canal;
Symptoms may include pain, itching, and discharge from the ear, hearing
loss, buzzing in the ear.
Prevention
There are a number of ways of avoiding otitis externa.
- drying the ear thoroughly after getting your ears wet
- avoiding swimming in polluted water,
- protecting the ear canal with cotton soaked with vaseline while
swimming or applying hair spray or hair dye.
†
|
 |
Diagnosis
The diagnosis
is made by listening to your symptoms and examining your ear.
The ear canal will usually appear red and swollen. Touching the outer ear may
increase pain. The skin of the ear canal may appear like eczema with scaly
skin.
Treatment
Ear drops or a spray containing antibiotics to fight infection and corticosteroids
to reduce itching and inflammation usually help.
If ear drops are used, they should be applied abundantly (four or five drops
at a time) since too much is harmless and very often they drip out of the ear.
(Follow the instructions supplied with your medication).
If the ear canal is very swollen, a wick may be applied in the ear to allow
the drops to travel to the end of the canal
Occasionally, oral medication in the form of antibiotics may be needed in more
severe cases.
Pain relief will help the pain/discomfort. If the pain is severe ask the chemist
for some strong painkillers.
Fungal infections may be treated with appropriate anti-fungal agents applied
to the external ear.
Applying warmth to the ears may reduce pain.
Protect ears from further damage so avoid the triggers if possible. Avoid wax
earplugs
Do not scratch the ears or insert cotton swabs or other objects in the ears.
Further
information
|
This article published on
04 December 2005
Next review date 12/1/2013
Categorie(s)
First aid
Allergies
Allergies
Areaof
the body
Eyes, ears, nose, throat
Male
or female?
Both |